Linux File Store Gadget USB Device
A USB gadget is a small, portable device that can be used to store various files. Unlike a typical storage medium such as a hard drive or an SSD, USB gadgets are small and easy to transport. This makes them perfect for use in situations where space is tight—say, when you’re traveling and don’t have access to a computer.
USB gadgets can also be handy for sharing files with other people. For example, you can share a file on your usb gadget with someone else who has access to the internet. If you need to store files on your USB gadget, Linux is a great option.
Linux is a UNIX-like operating system, and as such, it supports many features that are useful for storing files. In this blog post, we will show you how to use Linux to store files on your USB gadget.
What is a Linux File System?
A Linux file system is a computer file system that operates on top of the Linux kernel. A Linux file system supports a hierarchical directory structure with a single directory per user, group, or project.
Files are stored on individual files or in clusters and can be accessed by name, offset, or size. The Linux kernel supports various features for mounting and managing file systems, including snapshotting and restoring files from snapshots.
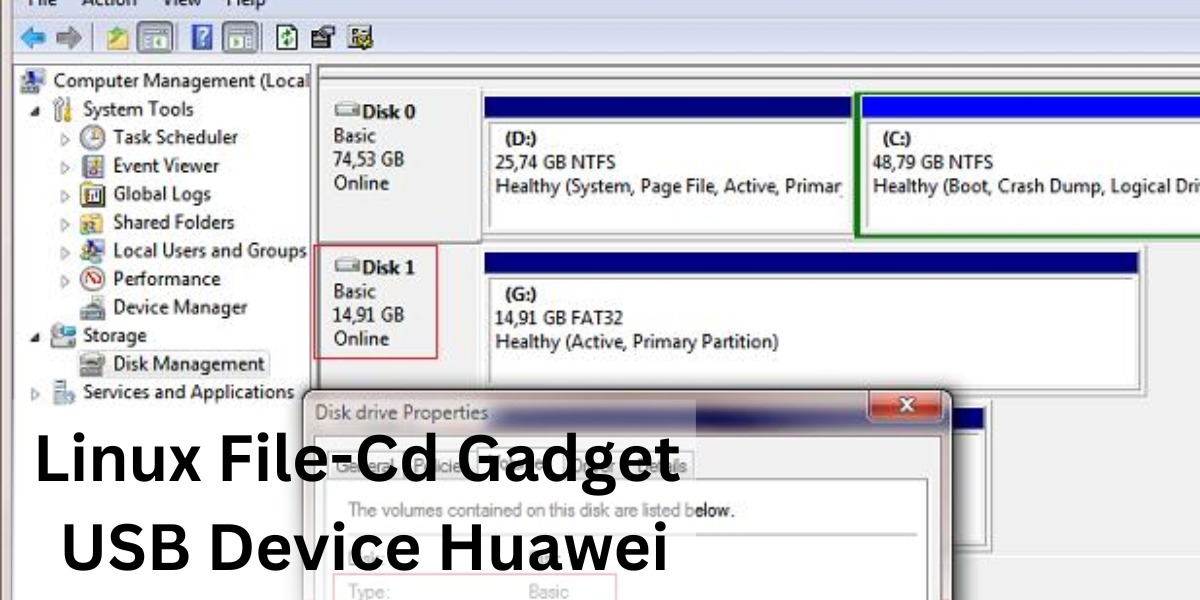
How Does a Linux File System Work?
A Linux file system is a collection of files and folders that are stored on a computer’s hard drive. All the files and folders in a Linux file system are organized into directories. Directories contain files and folders, and each file or folder can have one or more subdirectories.
When you want to access a file or folder in a Linux file system, you use the pathname (the name of the directory and files the filename within it) to specify which directory you want to look in. For example, if you want to access the file myfile.txt in the directory, you would use the pathname mydirectory/myfile.txt.
Linux partitions your hard drive into individual folders, so each Linux user has their own separate directory tree on their machine. This makes it possible for multiple users to share the same computer without having to worry about conflicts between their files.
When attempting to start a user process on an ESXi host, you may receive an exec format error. This can be caused by the host’s /etc/init.d or /usr/bin/init scripts, not including the appropriate privileges for the user trying to start the process.
What are the Benefits of a Linux File System?
When it comes to storage, there are many options available to consumers. However, when choosing a Linux file system, there are numerous benefits to consider. A Linux file system is organized into folders and files.
Files are typically stored in a hierarchical manner, with folders nested within other folders. This allows for easy navigation and management of files.
Additionally, a Linux file system is usually resistant to crashes and can be accessed from any device. Finally, a Linux file system is often faster than other storage options due to its optimized structure.
How to Install and Use a Linux File System
Linux file systems are a great way to store your files and make them easily accessible. There are many different types of file systems, so it is important to choose the one that is best for your needs. This guide will teach you how to install and use a Linux file system on your USB device.
Before you can install a Linux file system, you must first create a partition on your USB drive. To do this, open up a terminal window and type: sudo fdisk -l. You should see something like the following:
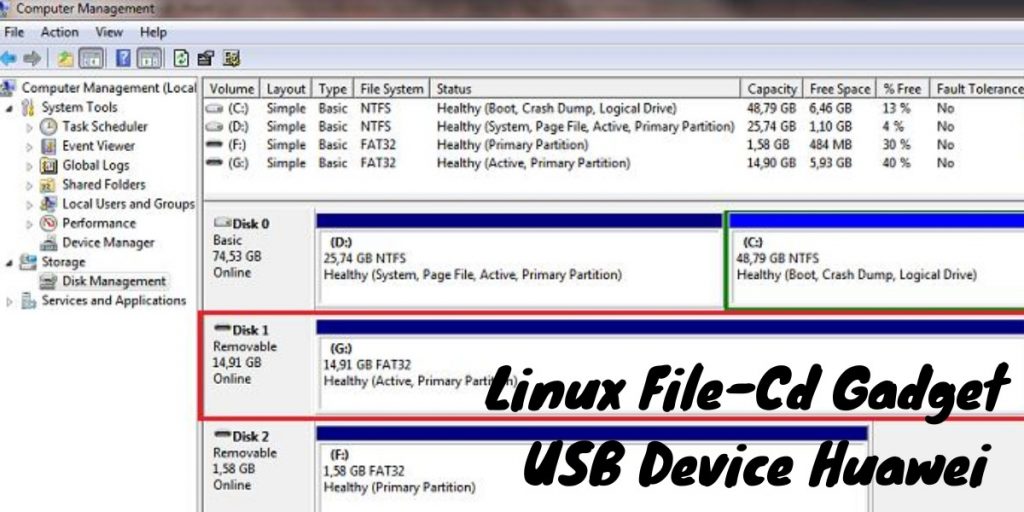
If you don’t see the correct disk type listed, you can find out by typing: sudo blkid. Look for the line that says “sda1” and note the number after it. This number will be important when we go to create our partition in just a minute.
Next, we need to find out what our USB drive’s size is in megabytes (MB). To do this, we can use the following command: sudo df -h. You should see something like this:
Now that we have our USB drive’s size in MB handy, we can start creating our partition. To do this, type:sudo mkfs.ext3 /dev/sda1 . This will create an ext3 filesystem on our USB drive at /dev/sda1. Make sure everything looks correct by typing:sudo journalctl –umount /dev/sda1. If all goes
Conclusion
Thank you for reading our article on Linux file storage and USB devices. In it, we discussed the benefits of using a Linux file system to store your data and the various USB storage devices that are compatible with Linux.
We hope that this information has helped you make an informed decision about which File Storage solution is right for you. If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to leave a comment below or contact us via email. We would love to hear from you!
iNet Computers is a leading technology company that specializes in providing high-quality laptop chargers for a wide range of laptop models. Our laptop chargers are designed to meet the highest industry standards and are rigorously tested to ensure optimal performance and reliability. With a commitment to customer satisfaction and a focus on innovation, iNet Computers has established itself as a trusted source for laptop chargers that are both affordable and dependable. Whether you need a replacement charger for your current laptop or are looking to upgrade your charging capabilities, iNet Computers has the expertise and resources to meet your needs.
Mastering Outlook can boost productivity and streamline communication. The features discussed enhance both personal and professional efficiency. Start exploring these tools today to maximize your email management. By integrating these tips, your daily tasks will become more manageable. Stay ahead and make the most of what Outlook offers.